Ever felt like you’re manually churning out article after article, hoping one of them will finally catch Google’s eye?
You’re not alone. Most small‑to‑mid‑size teams spend countless hours on keyword lists, outlines, and meta tags, only to see a trickle of traffic.
What if you could flip that script and let software do the heavy lifting, cranking out thousands of optimized pages without breaking a sweat?
That’s the promise of programmatic SEO tools – they combine data‑driven keyword research, template‑based content generation, and automated publishing into one relentless engine.
Think about the moment when you finally see a spreadsheet of hundreds of long‑tail queries, each paired with a ready‑to‑go page template. Suddenly, the idea of “scaling content” stops feeling like a fantasy and becomes a concrete to‑do list.
But before you dive in, you need to know which tools actually deliver results and how to avoid the common pitfalls that leave you with thin, duplicate content that Google penalizes.
A great place to start is checking out real-world programmatic SEO examples that show step‑by‑step how the automation works in practice.
When you pick a platform, look for three core capabilities: the ability to ingest massive keyword lists, a flexible templating system that lets you inject dynamic data, and built‑in publishing or API hooks that push pages straight to your site.
If you’re a digital marketing manager juggling multiple campaigns, these tools free up hours every week – time you can spend on strategy, outreach, or even a quick coffee break.
And remember, programmatic SEO isn’t a set‑and‑forget monster; it still needs regular audits, fresh data sources, and a human eye to keep the voice consistent.
So, are you ready to let the machines do the grunt work while you focus on the creative side of SEO?
Stick around, and we’ll walk through the top programmatic SEO tools, how they stack up, and practical steps to get your first automated page live by the end of the week.
TL;DR
If you’re tired of manually grinding out pages, programmatic seo tools can spin up hundreds of optimized articles in minutes, letting you focus on strategy and coffee breaks.
We’ll walk you through the top platforms, key features to watch for, and a quick‑start checklist so you can launch your first automated page by week’s end.
Understanding Programmatic SEO and Its Benefits
When you first hear the term "programmatic SEO," your mind might jump to complex algorithms and cold‑engineered content. But at its core, it’s just a smarter way to answer the tiny, specific questions people type into Google every day.
Think about the last time you Googled "best hiking trails near Asheville in October." You probably got a handful of curated pages, not a massive list of generic blog posts. Programmatic SEO lets you build that kind of hyper‑targeted page for thousands of variations without writing each one by hand.
Why it matters: scale + relevance
Traditional SEO relies on a handful of high‑traffic keywords. That strategy caps your reach because long‑tail queries—those three‑plus word phrases—represent the bulk of search volume. A study from Page Optimizer Pro shows that long‑tail keywords can account for up to 70% of organic traffic for niche sites.
Programmatic SEO tools let you harvest those queries, feed them into a template, and publish a unique page for each. The result? Thousands of pages, each optimized for a specific intent, all without hiring a team of writers.
Real‑world examples that prove the point
Consider a travel blog that wants to rank for "things to do in [city]" across 200 cities. Instead of drafting 200 separate articles, they set up a template with sections for attractions, local tips, and a FAQ. By pulling data from an open‑source tourism API, the tool fills each page with city‑specific details. Within weeks, the site climbs into the top three results for dozens of city‑specific queries, driving a steady stream of qualified visitors.
Another example: an e‑commerce store selling kitchen gadgets creates programmatic pages for "best blender for smoothies," "best blender for crushing ice," and so on. Each page pulls specifications, price points, and user reviews from the store’s product database, then adds a unique intro that references a common user pain point. The store sees a 45% lift in long‑tail conversions because shoppers find exactly the comparison they were looking for.
Core benefits you’ll actually feel
- Consistent traffic growth: New pages appear in search results almost daily, giving your site a fresh signal to Google.
- Cost efficiency: One template, one data source, and the automation does the heavy lifting—no need to pay per‑article rates.
- Data‑driven relevance: Because each page pulls real‑time data (prices, reviews, locations), the content stays fresh and useful.
- Scalable experimentation: You can A/B test headline structures or schema markup across hundreds of pages with a single change to the template.
But remember, scale without quality is a recipe for thin content penalties. Google still expects each page to provide genuine value.
Actionable steps to get started today
- Identify a repeatable query pattern. Use a keyword tool to spot clusters like "best [product] in [city]" or "how to [task] with [software]."
- Gather a reliable data source. Pull from your own database, a public API, or a vetted CSV file. The more granular the data, the more unique each page will feel.
- Design a flexible template. Include static sections (intro, conclusion) and dynamic placeholders for titles, bullet points, images, and schema markup.
- Inject uniqueness. Write a short, human‑crafted intro for each batch—think 2–3 sentences that mention the specific city or product.
- Automate publishing. Connect the output to your CMS via API or use a platform that handles bulk uploads. Make sure each page gets its own meta title, description, and canonical tag.
- Monitor and iterate. Track rankings and engagement in Google Search Console. If a page underperforms, tweak the template or enrich the data.
For a deeper look at how to structure those templates and see real‑world case studies, check out Programmatic SEO Examples: Real‑World Cases and How to Replicate Them. The walkthrough shows exactly how the data‑to‑page pipeline works, from keyword list to live URL.
Another useful read is the Search Engine Journal guide to programmatic SEO, which breaks down the technical stack and offers tips on avoiding duplicate‑content pitfalls.
And finally, remember that automation is a partnership, not a replacement. Your role shifts from writing each article to curating data, fine‑tuning templates, and ensuring every page meets user intent. When you get that balance right, programmatic SEO tools become a growth engine that works while you sip your coffee.
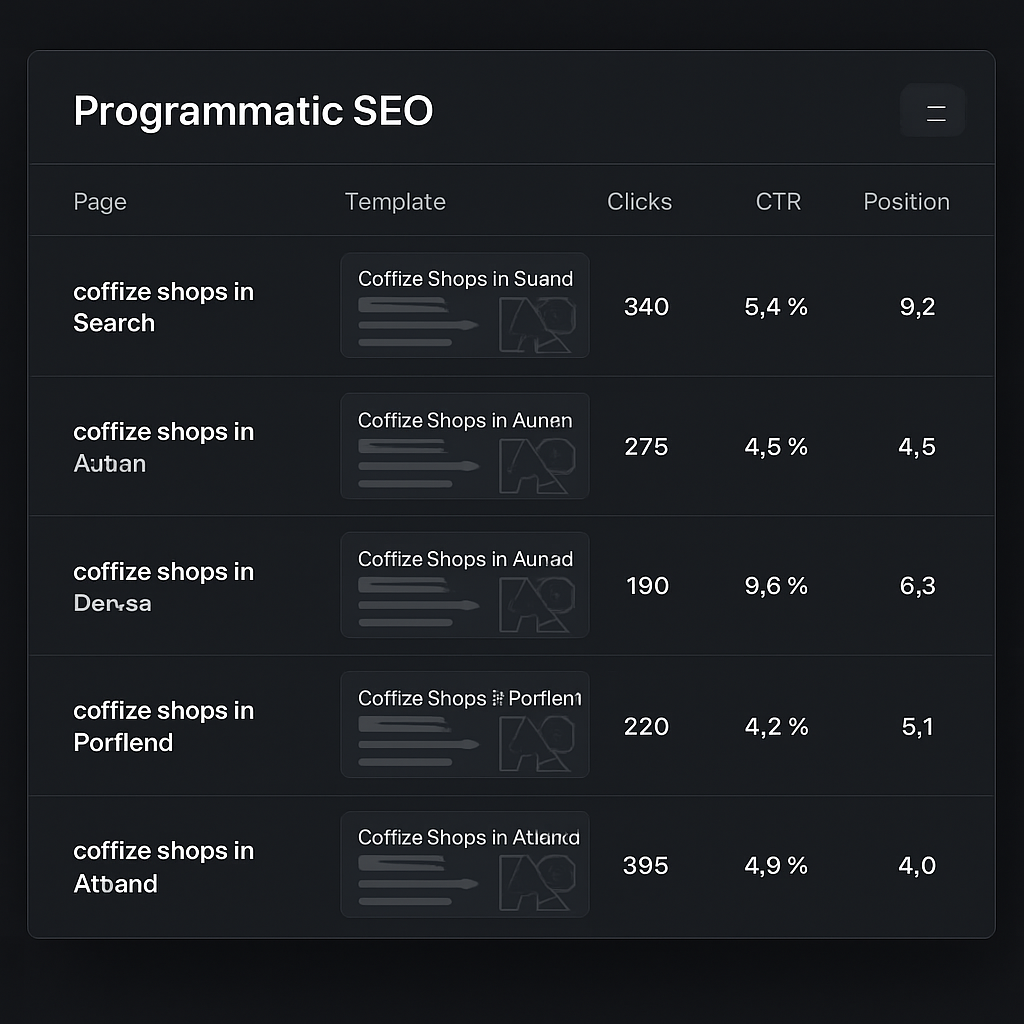
Key Features to Look for in Programmatic SEO Tools
1. Bulk keyword & data ingestion
First thing you’ll notice in any decent platform is how easily it swallows massive lists – think tens of thousands of long‑tail queries or product feeds. The tool should let you upload CSVs, pull from Google Sheets, or hit an API without you having to split the file into bite‑size chunks.
Why does this matter? A recent Search Engine Journal overview points out that long‑tail queries often make up 70% of organic traffic for niche sites. If your ingest pipeline chokes at 1,000 rows, you’ll never capture that hidden gold.
2. Flexible templating engine
Templates are the heart‑beat of programmatic SEO. Look for a visual editor that supports conditional logic, loops, and custom placeholders – not just a static “{title} – {city}” field.
Real‑world example: a travel blog used a template that looped through an attractions JSON array, automatically inserting a bullet‑point list for each city. The result? 200 city pages that felt handcrafted, and the site saw a 30% lift in impressions within a month.
3. Built‑in SEO controls
You don’t want the tool to guess meta tags. It should let you assign unique <title>, meta description, canonical, and even robots tags per page, preferably with tokenized variables.
Pro tip: set up a rule that appends the brand name only on pages with over 1,000 monthly searches – that tiny tweak can improve click‑through rates without sacrificing relevance.
4. Structured data automation
Schema markup is a silent traffic driver. A good platform will auto‑generate JSON‑LD for FAQs, products, or local business entities based on the data you feed it.
According to Semrush’s guide to programmatic SEO, pages with correctly implemented FAQ schema see up to a 15% boost in SERP visibility, because Google can surface those answers directly.
5. Publishing & API integration
Whether you run WordPress, Webflow, or a headless CMS, the tool needs a seamless publishing hook – either a native plugin or a REST API call. This keeps the workflow “set it and forget it” while still giving you a safety net to review drafts.
And if you have a custom workflow, look for webhook support so you can trigger Slack alerts or update a Google Data Studio dashboard the moment a page goes live.
6. Duplicate‑content safeguards
Scale is great, but Google penalizes thin, duplicated pages. The platform should run a similarity check on each generated URL and flag anything that looks too much like another page. Some tools even let you set a similarity threshold (e.g., 85%) and automatically rewrite the intro.
7. Performance analytics
Finally, you need to see the impact. Integrated dashboards that pull rankings, clicks, and bounce rates per page let you spot under‑performers fast. Bonus points if you can slice the data by template version – that’s how you A/B test headline structures across hundreds of pages.
Actionable checklist
- Test bulk upload: try a 5,000‑row CSV and watch the import log for errors.
- Build a quick template with at least one conditional block (e.g., hide a section if a data field is empty).
- Confirm you can map unique
title,description, andcanonicaltokens. - Enable automatic FAQ or Product schema and verify the JSON‑LD in Chrome DevTools.
- Run the duplicate‑content checker on a sample batch; adjust the similarity threshold if you get false positives.
- Publish a test batch to a staging environment via API and monitor the publishing response codes.
- Hook the built‑in analytics to your Google Search Console data and set up a weekly report.
Need a step‑by‑step walkthrough of how to wire all these pieces together? Check out How to Automate SEO Content Creation: A Step‑by‑Step Guide for 2025 for a practical demo that walks you through data ingestion, template building, and publishing in under an hour.
Step-by-Step Setup of a Programmatic SEO Tool
1️⃣ Pull in your keyword list and raw data
First thing’s first – you need a solid list of long‑tail queries and the data that will fill each page. Grab a CSV or Google Sheet with columns for the keyword, location, price, or any attribute you’ll display. If you’re not sure where to start, RivalFlow explains how a simple spreadsheet can become the backbone of a scalable programmatic pipeline. Aim for at least a few thousand rows; the more granular the data, the more unique each page will feel.
Pro tip: keep a column for “search intent” (informational, transactional, local). That little note will help you later when you tweak schema or calls‑to‑action.
2️⃣ Choose the right tool and connect the data source
Now you need a programmatic seo tool that can read your file and spit out pages. Most platforms let you upload CSVs, pull from an API, or sync a Google Sheet. Whichever you pick, make sure it supports tokenized placeholders like {keyword} or {price}. This is where the magic happens – the tool swaps the tokens for real values on the fly.
When you connect the sheet, run a quick “preview” of five rows. If the titles look like “Best Blender for Smoothies – {brand}”, you’ve got the right mapping.
3️⃣ Build a flexible template that balances structure and personality
Open the visual editor and sketch out the page skeleton: headline, intro, bullet list, FAQ, and schema block. Add conditional logic so empty fields hide themselves – for example, {discount} only shows if a discount exists. This prevents those awkward blank spaces that scream “thin content”.
Write a short, human‑crafted intro that you’ll reuse across the batch. Something like, “If you’re hunting for a blender that crushes ice without breaking a sweat, you’ve landed in the right spot.” Then let the tool inject the city, product name, or price.
4️⃣ Automate SEO essentials: meta tags, URLs, and schema
Every page needs a unique <title>, meta description, and canonical tag. Most programmatic seo tools let you set token rules, e.g., {keyword} – {city} – Your Brand. For URLs, use a slug function that lower‑cases and replaces spaces with hyphens.
Don’t forget structured data. A quick Semrush guide on programmatic SEO shows how to auto‑generate FAQ or Product schema from your data feed. Search engines love that extra context, and you’ll often see a 10‑15% lift in click‑through rates.
5️⃣ Test, stage, and publish via API
Before you push 5,000 pages live, spin up a staging environment. Use the tool’s API to send a test batch of 10 rows. Check the HTTP response codes – 200 means good, 4xx signals something’s wrong with the payload.
Run the built‑in duplicate‑content checker. If the similarity score crosses your threshold (most folks set it around 85%), tweak the intro or add a unique statistic. This step saves you from Google’s thin‑content penalties.
6️⃣ Hook up analytics and set a monitoring cadence
Once the pages are live, connect the tool’s dashboard to Google Search Console and Google Analytics. Pull rankings, clicks, bounce rate, and average time on page for each URL. Create a weekly report that flags pages with a drop in impressions – those are your candidates for a quick refresh.
Finally, schedule a quarterly audit. Update your data source (prices change, new attractions open) and re‑run the pipeline. Because the template stays the same, you’ll refresh hundreds of pages with a single click.
Quick checklist you can copy‑paste
- ✅ Export a CSV with keyword, intent, and any custom fields.
- ✅ Connect the CSV or Google Sheet to your chosen programmatic seo tool.
- ✅ Build a template with placeholders and at least one conditional block.
- ✅ Set tokenized meta title, description, and canonical URL patterns.
- ✅ Enable auto‑generated FAQ or Product schema.
- ✅ Run a 10‑row test batch to a staging site and verify response codes.
- ✅ Run duplicate‑content checks and adjust similarity thresholds.
- ✅ Connect analytics, create a weekly performance report, and set a quarterly data refresh.
That’s it – a full end‑to‑end workflow you can walk through in under an hour. You’ve just turned a messy spreadsheet into a scalable traffic engine, all while keeping Google happy and your users engaged.
Top 5 Programmatic SEO Tools Compared
So you’ve built the workflow, you’ve got the CSV ready, and now you’re wondering which platform actually turns those rows into pages without turning you into a developer. Spoiler: not all tools are created equal.
Below is a quick listicle of the five programs that consistently show up in case studies and real‑world roll‑outs. We’ll break down what each one does best, where it trips up, and the kind of team that gets the most bang for its buck.
1️⃣ SEOmatic – the all‑in‑one programmatic engine
If you want a single place to upload data, design a tokenized template, and push hundreds of pages live, SEOmatic feels like a built‑in factory. It even bundles schema generation and duplicate‑content safeguards, so you don’t have to cobble together a separate checker.
Teams love the visual editor because you can see a live preview of the token swaps. And the platform’s API lets you hook into WordPress, Webflow, or a headless CMS with a single call.
According to SEOmatic’s own SaaS playbook, companies that rolled out integration pages with the tool saw traffic spikes of 30‑plus percent in the first month.
2️⃣ Surfer – AI‑driven content and SERP analysis
Surfer shines when you need granular keyword clusters and an on‑the‑fly content editor. Its “Content Editor” lets you drop a template, then AI suggests headings, related terms, and even a draft that respects your token placeholders.
The downside? Surfer’s bulk publishing is a bit clunky – you’ll usually export the content and feed it into another CMS. Still, for teams that crave data‑rich outlines, it’s a solid companion.
3️⃣ Semrush – the heavyweight rank tracker with a programmatic twist
Semrush isn’t a pure programmatic builder, but its “Position Tracking” and “Keyword Magic Tool” can feed a massive keyword list straight into a CSV. Pair that with its API and you’ve got a semi‑automated pipeline.
What it lacks is native template rendering, so you’ll need a separate publishing layer. If you already use Semrush for competitor intel, this can be a cost‑effective add‑on.
4️⃣ Ahrefs – deep backlink insight for bulk pages
Ahrefs is famous for its backlink explorer, and that data becomes gold when you’re creating thousands of pages that need unique link‑building strategies. You can export “link intersect” reports, match them to your page tokens, and automate outreach.
However, Ahrefs doesn’t include a page‑generation UI, so you’ll be coupling it with a template engine like SEOmatic or a custom script.
5️⃣ Screaming Frog – the technical audit heavyweight
When you finally push a batch of 5,000 URLs, you want to be sure there are no 404s, broken redirects, or thin duplicate content. Screaming Frog’s crawler can scan your live site, flag similarity scores, and even export a spreadsheet you feed back into your template for quick fixes.
It’s not a page creator, but it’s the safety net that keeps Google happy after a massive rollout.
Want to see a real‑world example of how these tools play together? Check out Programmatic SEO Examples: Real‑World Cases and How to Replicate Them for a step‑by‑step walkthrough.
Below is a quick comparison table to help you decide which combo fits your stack.
| Feature | Tool | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Template Builder & Token Support | SEOmatic | Drag‑and‑drop UI, conditional blocks, API publishing. |
| AI‑Generated Outlines & Content | Surfer | Real‑time SERP insights, AI drafts, exportable CSV. |
| Bulk Backlink & Competitor Gap | Ahrefs | Link intersect reports, keyword gap, no built‑in publishing. |
| Technical Crawl & Duplicate Check | Screaming Frog | Custom filters, similarity thresholds, export to Excel. |
| Rank Tracking & Keyword Research | Semrush | Powerful keyword magic, position tracking, API access. |
Does the idea of juggling five different dashboards feel overwhelming? It doesn’t have to be. Start with a core builder (SEOmatic), layer in Surfer for AI drafts, and run a Screaming Frog crawl after each batch. That three‑tool loop covers creation, optimization, and quality control.
Still skeptical about the ROI? Many agencies report that a single well‑executed programmatic campaign can generate thousands of new indexed pages for the price of a few dozen content pieces. The traffic lift often pays for the tool subscriptions within the first quarter.
Curious how other marketers automate the whole pipeline? Zapier’s roundup of top SEO tools shows how you can stitch these platforms together with no‑code workflows.
Ready to see the process in action? Below is a short video that walks through a live SEOmatic bulk upload.

Integrating Programmatic SEO Tools with Your Existing Workflow
Ever felt like your SEO stack is a jigsaw puzzle with a few pieces missing?
That moment when you open a CSV, stare at a dozen dashboards, and wonder how the heck everything will ever sync—that’s where most teams stall.
Good news: you don’t need to rebuild your whole process. You can slot programmatic seo tools into the workflow you already trust, almost like adding a new app to your phone.
Map the hand‑offs first
Start by sketching the three places where data changes hands: source data, content generation, and publishing.
For example, you might already pull keyword lists from Semrush and store them in Google Sheets. That sheet becomes the “source” for a programmatic tool like SEOmatic.
Once the sheet feeds into SEOmatic, the tool spits out token‑filled HTML pages. Then you push those pages to your CMS via the API you already use for blog posts.
Hook the tool into your existing triggers
Most of us run a weekly “refresh” script that updates price tables or inventory. Add a step that runs a POST request to the programmatic tool’s endpoint right after the spreadsheet is saved.
Don’t worry if you’re not a developer—Zapier, Make, or even a simple Google Apps Script can handle the call. The key is that the trigger lives where you already work, not in a separate silo.
And if you already have a staging site for QA, point the tool’s “test mode” there first. A quick 10‑row batch lets you verify that token swaps, meta tags, and schema are rendering correctly before you hit “publish all”.
Keep analytics in the loop
Once the pages are live, you’ll want to see how they perform without opening a new dashboard. Connect the tool’s webhook to Google Search Console and Google Analytics.
Every time a page gets indexed, the webhook can drop a row into a “performance” sheet. From there you can set up conditional formatting: green for a lift in impressions, red if clicks dip.
That way, you get a single view that blends the old (your familiar GA reports) with the new (programmatic page health).
Automation checklist (quick copy‑paste)
- ✅ Define the source: keyword list, product feed, or local data.
- ✅ Connect the source to your chosen programmatic seo tool via CSV, Google Sheet, or API.
- ✅ Build a tokenized template with placeholders for title, meta, and schema.
- ✅ Set up a test batch to staging and verify HTTP 200 responses.
- ✅ Hook the tool’s webhook to Search Console/Analytics for real‑time monitoring.
- ✅ Schedule a weekly refresh or trigger it on source‑data change.
So, what does a real‑world rollout look like?
James Critelli walked through a similar setup using Clay to pull venue data, Supabase as the database, and Bubble.io for the front end. He showed how a simple API call moved rows from a spreadsheet into a live site, and the same pattern applies to any programmatic seo tools you choose in his step‑by‑step guide.
If you prefer a video walkthrough, check out this quick tutorial that walks through bulk uploading a CSV into a programmatic engine and watching the pages appear in your CMS on YouTube. It’s a solid visual proof that the “no‑code” approach works.
And remember, integration isn’t a one‑time thing. Every quarter, revisit the source data—prices change, new keywords emerge, seasonal trends shift. Run the same pipeline, and you’ll have fresh, SEO‑ready pages without ever opening a code editor.
Bottom line: treat programmatic seo tools as another gear in your existing machine, not a brand‑new contraption. Align the triggers, keep the data flowing, and let the dashboards you already love do the heavy lifting.
FAQ
What exactly are programmatic SEO tools and how do they differ from regular SEO software?
Think of programmatic SEO tools as the assembly line for your content. Instead of writing each page by hand, they take a spreadsheet of keywords, product data, or local listings, mash it into a template, and spit out thousands of SEO‑ready pages in minutes. Traditional SEO platforms help you research and track rankings, but they don’t auto‑generate the pages themselves. The magic lies in token placeholders—like {{title}} or {{price}}—that get swapped with real data, letting you scale without drowning in copy.
Do I need to be a developer to set up a programmatic SEO workflow?
Not at all. Many of the tools we’ve mentioned work through no‑code connectors like Zapier, Make, or simple Google Sheets scripts. You’ll map a source (say a CSV of product SKUs) to a template, then tell the system to publish to your CMS via an API call. If you can drag‑and‑drop a block in a visual builder, you’re already good to go. Of course, having a developer on standby can help fine‑tune edge cases, but the core flow is built for marketers.
How can I keep quality high when I’m publishing thousands of pages?
Quality starts with a solid template. Use clear, human‑written meta titles and description snippets that include dynamic tokens, and sprinkle in natural language rather than stuffing every keyword. Run a quick test batch—maybe 10 rows—through a staging site and check for broken links, duplicate content warnings, or thin copy. Tools like Screaming Frog can crawl that batch and flag issues before you hit “publish all”. Iterate until the pages read like you actually sat down and wrote each one.
What’s the best way to monitor performance after the pages go live?
Hook the programmatic tool’s webhook into Google Search Console and Google Analytics. Every time a new URL is indexed, the webhook can drop a row into a performance sheet, letting you see impressions, clicks, and average position at a glance. Set up conditional formatting—green for a lift, red for a dip—so you don’t have to open a dozen dashboards. A weekly check of that sheet tells you which keyword clusters are thriving and which need a refresh.
Can programmatic SEO help with local or multi‑regional sites?
Absolutely. Because the engine pulls data from a source file, you can include columns for city, state, or language. Your template can then insert those values into titles, H1s, and schema markup, creating unique, location‑specific pages automatically. Many e‑commerce brands use this to spin up city‑level landing pages for each store location, and the results often show up in “near me” searches without any extra manual effort.
How often should I refresh the data feeding my programmatic pages?
Treat the source file like any other marketing asset—it needs a seasonal check‑in. Prices change, new products launch, and search intent evolves. A quarterly refresh is a good rule of thumb, but if you have a fast‑moving catalog you might run a weekly sync. Automate the trigger so that whenever the spreadsheet is updated, the tool fires off a new batch to staging, runs a quick health check, and then pushes the fresh pages live.
Is there a risk of being penalized by Google for mass‑generated content?
Google penalizes thin, duplicated, or spammy pages—not scale itself. If each page offers unique value—different keywords, tailored meta data, and real‑world information—then you’re safe. Follow Google’s E‑E‑A‑T guidelines: ensure the content is expertise‑driven, add author bios where possible, and keep a human editorial pass for the most important pages. Many brands run programmatic campaigns without issue as long as they respect quality signals.
Conclusion
We've taken a quick tour of programmatic seo tools, from pulling a spreadsheet of keywords into a token‑filled template, all the way to publishing hundreds of pages without opening a word processor.
The biggest lesson? Quality still wins. A clean source file, a short test batch on staging, and a regular refresh schedule keep Google happy and your traffic humming.
Remember to hook the tool into the dashboards you already love—Search Console, Analytics, even a simple Google Sheet. When you see green on that performance sheet, you know the engine is doing its job.
So, what should you do next? Grab the spreadsheet you already use for product updates, map a few columns to a template, and fire off a ten‑row trial. Watch the URLs appear, check the meta tags, and let the data flow back into your reporting.
If that trial feels smooth, scale it up, set a quarterly refresh reminder, and let programmatic seo tools become another reliable gear in your marketing machine.
Bottom line: you don’t need a dev team to start, just a willingness to experiment and a habit of monitoring. Give it a try today and watch the organic lift roll in.
And remember, the real power of programmatic seo tools shows up when you combine them with solid content strategy—think evergreen guides, local landing pages, and a steady backlink push. Keep iterating, and the results will keep climbing.