Everyone knows medium tail keywords hit the sweet spot between broad and niche search terms.
But what are they, exactly?
In this guide, you'll get a complete cheatsheet to researching, mapping, and optimizing medium tail keywords for real SEO impact.
Some are perfect for striking a balance between volume and competition.
Some capture clear purchase intent without getting lost in ultra-specific queries.
Some adapt seamlessly to voice search and conversational queries.
Some reveal hidden opportunities that competitors overlook.
Some turn casual browsers into engaged readers and customers.
Let's dive right in.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Medium Tail Keywords
- Understanding Medium Tail Keywords
- Benefits of Targeting Medium Tail Keywords
- Researching & Identifying Medium Tail Keywords
- Mapping Keywords to Content
- Optimizing Your Content
- Measuring Success & Refinement
- Common Pitfalls & How to Avoid Them
- Advanced Strategies
- Conclusion
Introduction to Medium Tail Keywords
In the constantly evolving world of SEO, finding the right balance between broad and overly specific search phrases can feel like chasing a moving target. Enter medium tail keywords. These are multi-word phrases—typically two to four words—that offer a sweet spot in search volume, competition, and user intent.
Medium tail keywords combine the reach of short tail terms with the clarity of long tail queries. They often bring hundreds to a few thousand searches per month, making them high-potential targets for content that converts. In this introduction, we’ll highlight why medium tail keywords deserve a permanent spot in your SEO toolkit.
Understanding Medium Tail Keywords
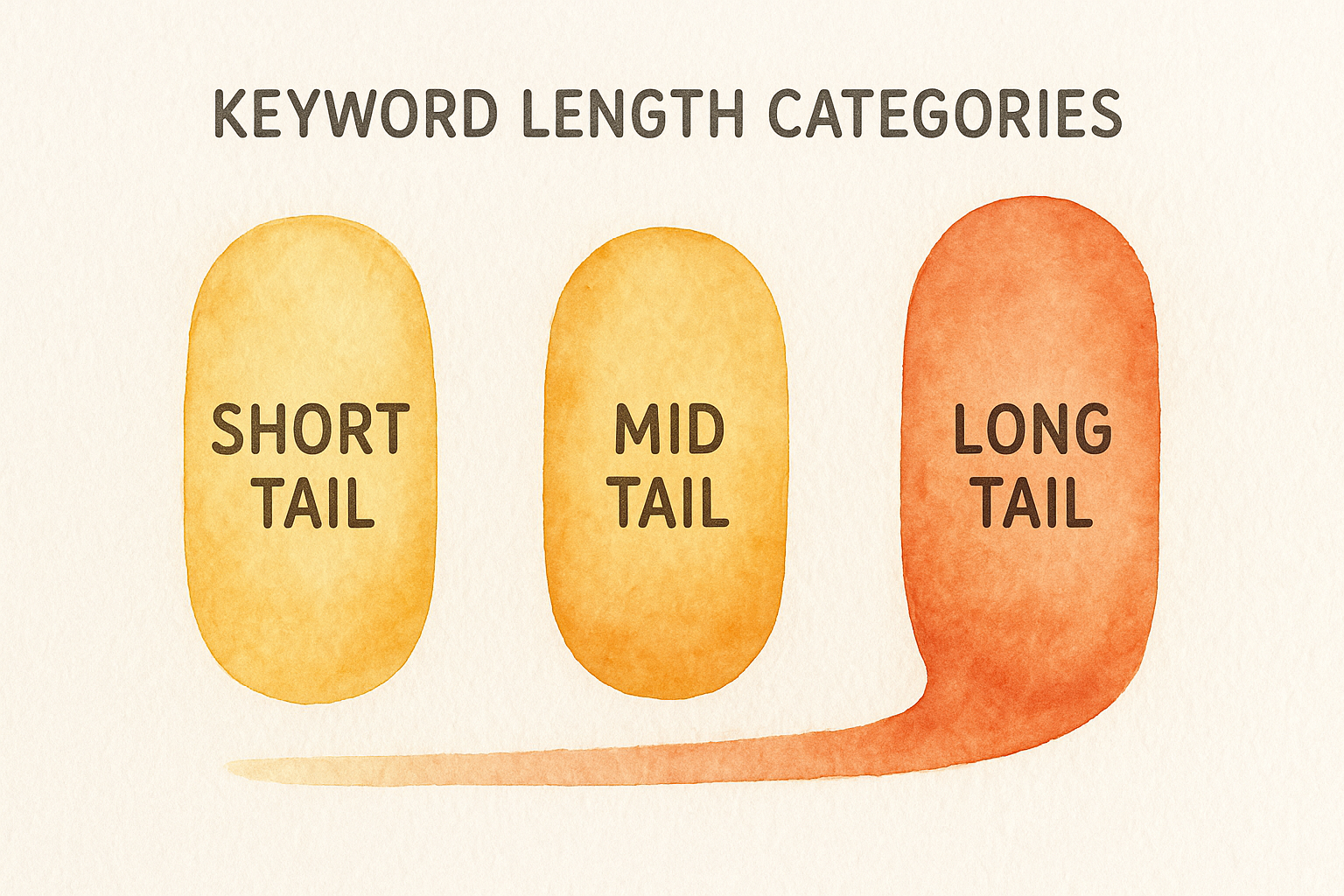
3.1 Definition of Tail Length Categories
Search terms are classified based on word count, specificity, and competition level:
- Short Tail (1–2 words): Very broad ("shoes", "marketing"); millions of searches monthly; fierce competition.
- Medium Tail (2–4 words): Balanced specificity ("running shoes men", "SEO tips 2025"); hundreds to thousands of monthly searches; moderate competition.
- Long Tail (4+ words): Highly specific ("best trail running shoes for flat feet", "SEO tips for non-profits 2025"); low volume; low competition.
According to Ceralytics, medium tail keywords capture clear intent without the resource drain of ultra-competitive short tail targets.
This segmentation is also illustrated well in community-sourced infographics (e.g., Reddit).
3.2 Why Medium Tail Keywords Matter
- Balanced Volume: Enough traffic potential to move the needle without unrealistic effort.
- Clear Intent: Searchers often know what they want—researching options or ready to purchase.
- Manageable Competition: Easier to rank for than broad head terms, yet more rewarding than obscure long tails.
For example, the term “best running shoes men” averages 1,200 monthly searches. It signals clear commercial investigation intent and has a Keyword Difficulty score below 40, making it a prime medium tail target.
Benefits of Targeting Medium Tail Keywords
4.1 Balanced Search Volume and Competition
Short tail keywords face stiff competition from established brands and require large budgets to rank. Long tails, while accessible, often trickle negligible traffic. Medium tail sits between these extremes:
- Rank with a modest backlink profile and quality content.
- Capture meaningful traffic without an enterprise SEO budget.
- Outperform purely long-tail pages by addressing broader queries.
4.2 High Conversion Intent
Medium tail queries often indicate a stage of commercial investigation. A search for “best budget trail running shoes” suggests the user compares products—a stage ripe for conversion-focused content, product reviews, or comparison charts.
4.3 Authority Building at Scale
By clustering medium tail topics, you can demonstrate topical depth. Google rewards sites that cover a topic comprehensively. Building pages around related medium tail terms boosts your site’s overall authority and rankings.
Researching & Identifying Medium Tail Keywords
5.1 Keyword Research Tools
To discover and evaluate medium tail opportunities, use:
- Google Keyword Planner: Free baseline for volume and cost estimates.
- SEMrush: Detailed keyword difficulty, traffic potential, and competitive analysis.
- Ahrefs: Volume trends, click estimates, and parent topic insights.
- Ubersuggest: Easy-to-use interface for free volume and CPC data.
Start broad, filter by monthly searches (e.g., 300–3,000), then sort by Keyword Difficulty. For more advanced comparisons of keyword research tools, see our in-depth guide.
5.2 Leveraging Google Search Features
Google itself offers free insights:
- Autocomplete: Type your seed term and note two- to four-word suggestions.
- People Also Ask: Extract recurring questions that hint at medium tails.
- Related Searches: At the SERP bottom, spot multi-word phrase ideas.
5.3 Competitor Analysis
Reverse-engineer top-ranking pages. Tools like Ahrefs and SEMrush reveal the medium tail phrases they target, content structure, and backlink profile. Then craft superior content by filling gaps and offering fresh insights.
5.4 Brainstorming & Customer Insights
Don’t rely solely on tools—talk to real users. Survey your audience, review support tickets, and explore forums. Many medium tail gems surface in customer phrasing rather than tool suggestions, as noted by SirLinkSalot.
Mapping Keywords to Content
Organize your keyword list into clusters. A pillar page covers a broad topic, while supporting posts target specific medium tails. This silo structure improves internal linking and signals expertise.
- Select a broad parent topic (e.g., “trail running shoes”).
- Assign related medium tail keywords (“best budget trail running shoes”, “trail running shoes for flat feet”) to individual posts.
- Link child posts back to the pillar page for contextual authority.
For vendors of DFY digital products, targeting medium tail keywords like “ready-made social media templates” can attract buyers seeking turnkey solutions.
Optimizing Your Content
7.1 On-Page SEO Best Practices
- Title Tags: Place the medium tail keyword near the beginning.
- Headings: Use H2–H3 variations and synonyms.
- Meta Descriptions: Craft a concise summary (120–160 chars) featuring the keyword.
- URL Structure: Keep it short and include your medium tail phrase.
- Image Alt Text: Describe visuals with the target keyword when relevant.
7.2 Creating In-Depth, User-Focused Content
Google favors content that thoroughly addresses user intent. Break your page into clear sections, add visuals, and answer common questions. Include FAQ blocks or step-by-step processes for snippet potential.
7.3 Semantic & LSI Keyword Integration
Use related phrases and synonyms to support your main medium tail term. Tools like LSIGraph or the “Searches related to” section in Google help you find Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) keywords.
7.4 Internal & External Linking Strategies
- Link to relevant pages within your site to distribute link equity and improve session depth.
- Cite authoritative external sources (studies, industry reports) to build trust.
Measuring Success & Refinement
8.1 Tracking Rankings & Traffic
Use Google Search Console and a rank tracker to monitor position changes for each medium tail keyword. Track month-over-month traffic trends to assess impact.
8.2 Monitoring Engagement Metrics
Analyze bounce rate, time on page, and scroll depth in Google Analytics. High engagement signals that your content meets user intent.
8.3 A/B Testing Headlines & CTAs
Experiment with title tag variations, H1s, and call-to-action buttons to boost click-through and conversions. Tools like Google Optimize or Optimizely simplify testing.
8.4 Iterative Keyword Expansion
Once you rank for initial medium tails, expand into adjacent topics by exploring related queries in comments, forums, and “People Also Ask.” This compounds traffic gains over time.
Common Pitfalls & How to Avoid Them
9.1 Over-Optimization & Keyword Stuffing
Resist the urge to cram your medium tail keyword into every sentence. Prioritize readability and natural flow.
9.2 Ignoring User Intent
Match content format to intent—informational, navigational, transactional, or commercial. A mismatch means high bounce rates and poor rankings.
9.3 Chasing Volume Over Relevance
High-volume medium tails may look attractive but often have fierce competition. Balance volume with difficulty and strategic fit.
Advanced Strategies
10.1 Voice Search Optimization
Voice queries tend to be conversational. Adapt some medium tail targets into natural-language questions (e.g., “what are the best trail running shoes for beginners”). Include Q&A blocks to signal relevance.
10.2 Structured Data & Rich Snippets
Implement schema markup for FAQs, HowTo, and product reviews. This can generate rich results and boost click-through rates dramatically.
10.3 International & Multilingual Targets
Localize your medium tail strategy for global markets. Use country-specific tools, translate phrases accurately, and adapt examples to local context.
Conclusion
Medium tail keywords are a powerful, often overlooked segment of the SEO keyword spectrum. They strike an ideal balance between search volume, competition, and user intent. By researching strategically, mapping topics through content silos, optimizing on-page elements, and continuously measuring and refining your approach, you can harness medium tail keywords to drive sustainable organic growth. Start integrating them into your content plan today to capture qualified traffic and outshine the competition.
